 Torsion Force
Torsion Force
The force works perpendicular to the centre line of the truss but is not positioned in the same plane as the centre line. This force tries to twist the truss. Here are some situations where...
 Transversal Force
Transversal Force
The transversal force is the force which works perpendicular to the centre line of the truss. The important situations for the transversal forces are as follows: 1. A heavy load on a short...
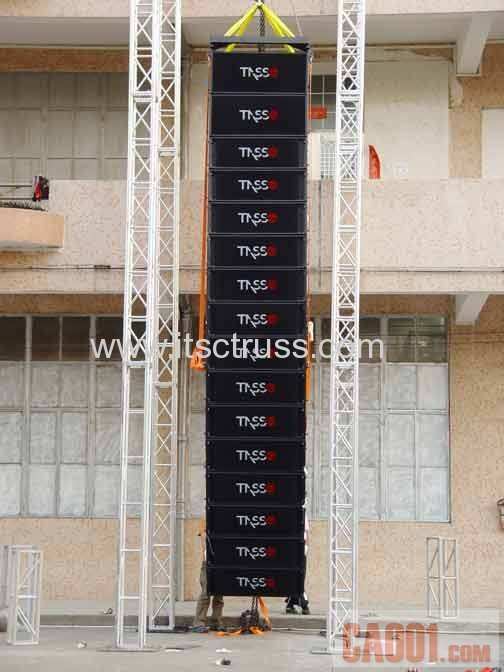 Bending Moment
Bending Moment
The Bending Moment is the sum of all the moments and reaction loads passing through the centre axis of the truss considered at any point,in one word, it is the force which is needed to deflect a...
 Normal Force
Normal Force
The normal force works longitudinal to the centre line of the truss.Below are examples of situations where a normal force occurs: 1. Towers. 2. Columns. 3. Rafter trusses on the roof. The...
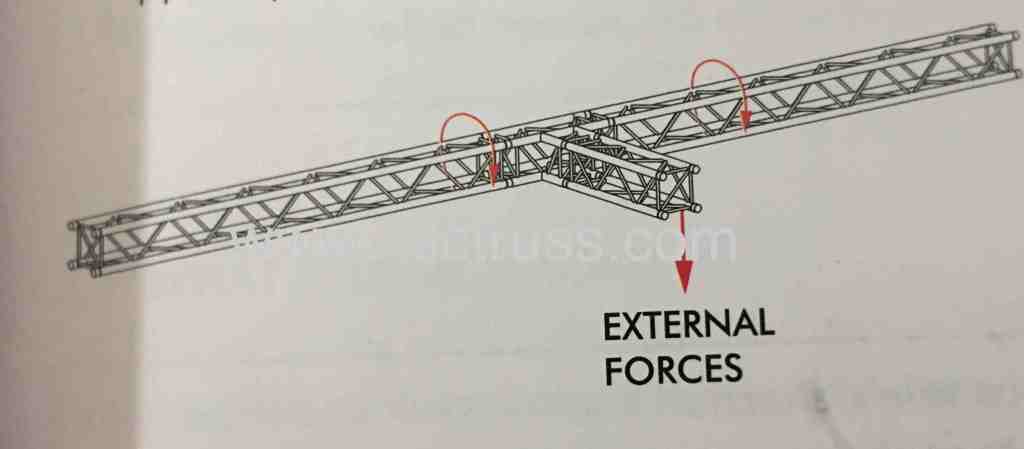
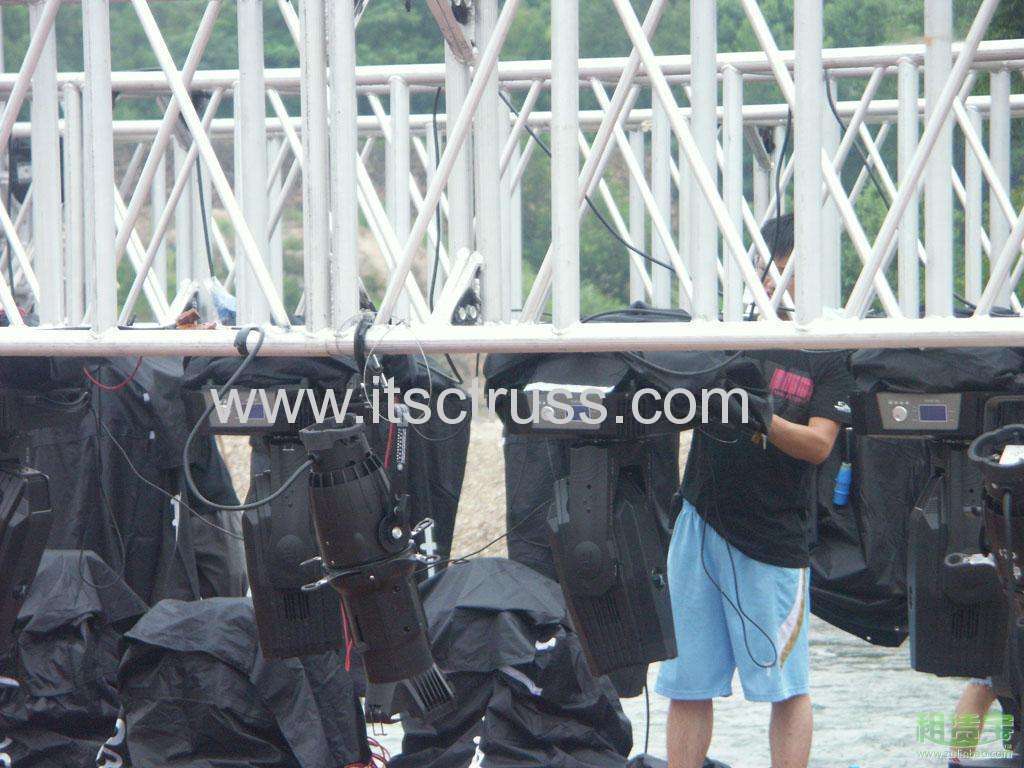 External and Internal Force
External and Internal Force
We can define mainly two forces on a truss: External and Internal Force. Main examples of the external forces are: 1. Live loading such as lighting fixtures, sound equipment, LED screen, ect. 2....
 Truss Feature
Truss Feature
Why the dominant feature of a truss is a triangular shape? Because the triangle can remain its shape when it is exposed to a load at connection point or joint points, even if the joints are hinged....
 Truss Connection
Truss Connection
There are 2 kinds of connection are in common use nowadays: Pin truss Trusses are connected with a solid double conical pin in the ends of the main tubes, and thepins exposed to double shear...
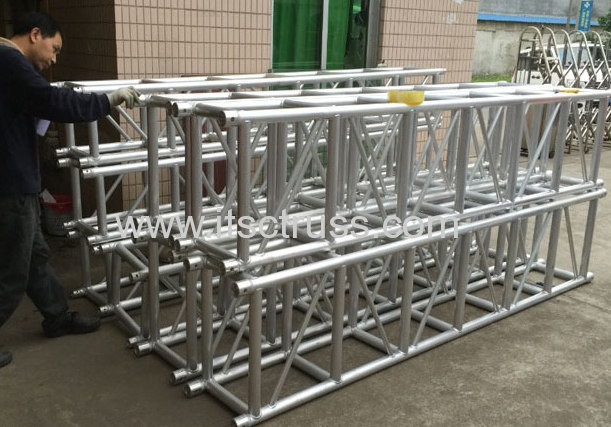 Truss Length
Truss Length
Trusses are usually made in standard lengths which can combine to other length as user required. Usually it is 2-3m (6-10ft ) long for one piece. However, longer length is usually needed. And the...
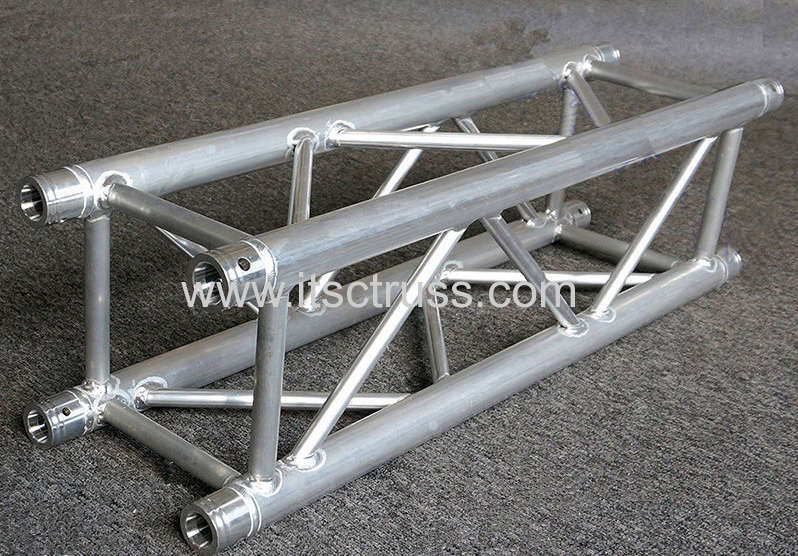 Truss Material
Truss Material
Why trusses are made of aluminum material? The reasons are as follows: 1. With a self-weight 65% less than steel, aluminum is very light 2. With corrosion resistant characteristic,aluminum needs...